Introducing PyTorch-Ignite's Code Generator v0.2.0
Authors: Jeff Yang, Taras Savchyn, Priyansi, Victor Fomin
Along with the PyTorch-Ignite 0.4.5 release, we are excited to announce the new release of the web application for generating PyTorch-Ignite's training pipelines. This blog post is an overview of the key features and updates of the Code Generator v0.2.0 project release.
Deep Learning As a Routine
In deep learning applications, neural networks are typically accompanied by code to preprocess the input and output data, visualize the results, define proper training and evaluation pipelines, and more. A significant part of this supporting code consists of reusable components, like data loaders, training loops, logging, and tracking. Therefore, deep learning practitioners usually organize their boilerplate codebases into collections of reusable components to speed up development.
PyTorch-Ignite is one such practical solution, a high-level library from the PyTorch ecosystem for training neural networks designed to simplify workflow development while maintaining maximum control, flexibility, and reproducibility. PyTorch-Ignite feels like a natural extension to PyTorch.
Ignite Your Training Pipelines
PyTorch-Ignite's Code Generator is an open-source tool developed to boost your training pipeline's scripts, carefully designed by PyTorch-Ignite's contributors to promote PyTorch-Ignite's best practices. The application has a user-friendly and intuitive web interface, simple enough for day-to-day use, and it is an excellent choice for quickly generating a custom templates for training PyTorch models.
In this release, we are using a new application development stack to enhance the user experience tenfold. For UI, we switched to a JavaScript stack. The PyTorch and PyTorch-Ignite specific generated code remains the same.
Getting Started
The best way to "ignite your training pipeline" is to visit Code Generator's homepage and select your task's template by clicking on the "Getting Started" button.
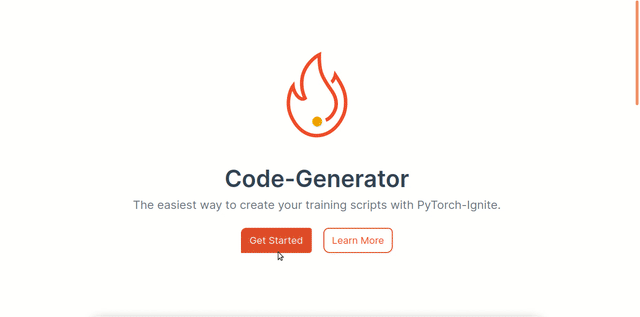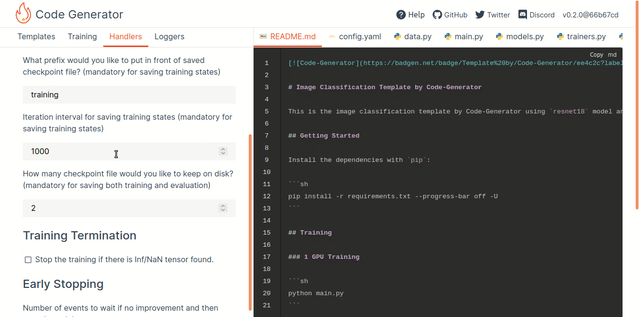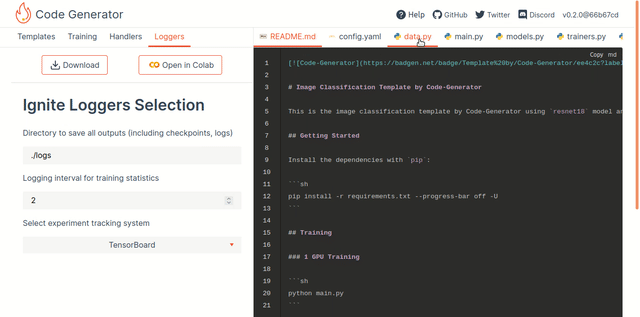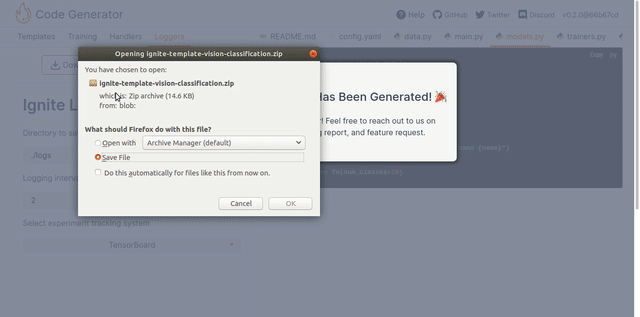
You can choose a template from a list of templates located on the left in the Templates tab. The app will start to render the template with the preconfigured default settings. You will see all the generated files with the rendered code on the right in different tabs as in a regular IDE. The current state of the configurations is reflected partially in the config YAML file.
Currently, we offer four customizable templates for widely used deep learning tasks: Vision classification and segmentation, Text classification, and DCGAN.
Start adjusting the code in the template by visiting different tabs on the left side:
- Training: To turn on Distributed training
- Handlers: To set up Checkpointing, Termination on NaNs, Early Stopping, etc
- Loggers: To configure Logging
Once you choose the appropriate settings, press the "Download" or "Open in Colab" button at the top to export generated code as a zip archive or a notebook, and follow any given additional steps. The resulting archive contains generated files bundled together. The requirements.txt file contains all the required dependencies, and the README contains all the necessary information for launching the script.
You are now ready to add in your data and model and run the code!
I Want To Contribute!
We encourage open source contributors from both frontend and data science communities to collaborate on the project. If you are interested, please visit the Contribution Guide. If you have any questions, do not hesitate to ask them on our Discord. Here are some good first issues.
Next Steps
In future releases, we plan to extend our template store and add more features, for example, configuration systems, data loaders, datasets and models, optimizers, and schedulers. We will continue improving the app's reliability and usability. To stay in touch, follow us on Twitter and Facebook. We would love to get your feedback on the project.
Acknowledgements
The development of this project is supported by a NumFOCUS Small Development Grant. We are very grateful to them for this support!
Comments